
23 Jan 2026 | INSIGHTS: Payroll management is a critical business function in Nepal, involving tasks such as...

7 Aug 2025 | INSIGHTS: Following up on our earlier insights on cases in Nepal’s First...

25 June 2025 | INSIGHTS: Cooperatives are member-owned and member-managed organizations...

10 June 2025 | INSIGHTS: From Silver Scams to Medical Negligence: Inside Nepal’s...

Nepal earned NPR 4.75 billion from eight carbon trading projects in October 2024. In the recent budget of F.Y. 2082/83 (25/26),...

The Budget for Fiscal Year 2082/83 Was Presented by Finance Minister Bishnu Prasad Poudel on 15 Jestha 2082 (29 May 2025). The Total Budget Size Is Npr 1960 Billion .

27 May 2025 | INSIGHTS:In Part 1 of this article, we explored the formulation stage of Nepal’s budget process - delving into the constitutional provisions, legal frameworks, and structured procedures that guide...

23 May 2025 | INSIGHTS: Get insights into Nepal’s FY 2082/83 budget process—from laws to ministry plans & Parliament review. See how transparency & goals shape national spending.

Cannabis has deep cultural and religious roots in Nepal, but it remains illegal under current law...

Explore key steps & legal criteria to convert a private limited to a public limited company in Nepal under Company Act 2063, plus post-conversion insights.

The Office of the Company Registrar issued the “Internal Control and Monitoring Directive, 2080 (2023)” on 16 Kartik 2080. This insight delves into how the directive aims to improve the quality of services, ensure company compliance with relevant laws, ultimately bolstering the credibility of company administration in Nepal.

Trademark and passing off are globally crucial for brand protection. In Nepal, the Patent, Design, and Trademark Act governs trademark registration, emphasizing exclusive usage rights. Nepal law and courts to an extent recognizes passing off for unregistered trademarks, fairly showcasing a commitment to safeguarding businesses.

In an era dominated by digital interactions, the Government of Nepal has taken a decisive step towards regulating and fostering self-regulation within the realm of social media. This article explores the details of the new Directive shaping social media regulations.

A brief on the Asset Management of Telecommunications Service Providers with Non-Existent Licence, 2079 (2022) laying out the procedures to expropriate the tangible and intangible assets held by telecommunication service providers with non-existent licence.

This brief explores the Nepalese Arbitration Act of 2055 (1999), shedding light on temporal boundaries in contractual matters and arbitration. It also delves into statutory time limits, offering insights through landmark cases within Nepal's legal landscape of dispute resolution.

Discover the main points of the 2017 Labour Act (2074) to understand the legal rules for obtaining services from employees through licensed agencies. Learn about the specific services provided by labor suppliers.

This publication emphasizes on the amendments made by the Securities Board of Nepal ("SEBON") through the Seventh Amendment of 2080 (2023) to the Securities Registration and Issue Regulations, 2073 (2016).

This guide explains employee layoffs and job cuts under Nepal's labor laws. It outlines the dos and don'ts during retrenchment, industry practices, and considerations for retrenching unionized employees.

The Nepal Rastra Bank has issued an official notice, dated 11 Bhadra 2080 (2023), which underscores the paramount importance of working capital loans by introducing some significant modifications in the "Working Capital Guidelines, 2079 (First Amendment) (2022).

This brief delves into the regulatory provisions and discretionary powers vested in the Labour Relation Committee for governing the usage of the Employee Welfare Fund, shedding light on the mechanisms guiding employee welfare.

This brief offers insights into the Company Act, 2063 (2006), elucidating the prerequisites and procedures for the registration, compliance, cancellation, and winding up of foreign companies in Nepal, providing a roadmap for their operations.

Evaluating the need for permanent establishment registration for foreign entities and to better understand the registration, criteria for transactions, exceptions to these criteria, significance of registration and complexities of tax implications for foreign entities in conducting business in Nepal.

This overview focuses on a framework for imposing direct taxes on the transaction value of digital services provided by non-resident individuals to Nepalese consumers. It highlights the taxation aspects of digital commerce in Nepal, introduced under Section 20 of the Finance Act, 2079 (2022). The economic landscape is rapidly evolving, and this measure aims to address the challenges.

This brief highlights the reforms brought by the Second Amendment of 2079 (2022) to the Company Directive, 2072 (2015) which was formulated by the Office of the Company Registrar in order to implement the Company Act efficiently and conduct company administration-related work effectively and systematically.
Highlighting the Startup Enterprise Fund Procedure, 2079 (2023), approved on 10 Falgun 2079 (22 February 2023), which streamlines the process of granting concessional loans to startups, prioritizing simplicity, transparency, and effectiveness in its operations.

Social Security in Nepal is a government-run program that provides financial assistance to citizens in the form of pensions, disability benefits, and survivor benefits. The program is funded through contributions from workers, employers, and the government. It is administered by the Ministry of Labour, Employment, and Social Security.

The National (Muluki) Civil Procedure Code, 2074 (referred to as the "Code"), introduced in 2017, has led to increased stringency by courts and regulators in enforcing compliance with Section 36 of the Code.

Nepal’s robust judicial system manages diverse case categories, each meticulously designated with specific reference codes. These codes seamlessly integrate into the daily court cause lists, enhancing the efficiency of legal proceedings and facilitating organized and streamlined administration within the country’s courts.

The pathway for Non-Resident Nepalese (“NRN”) to acquire Non-Resident Nepalese Citizenship in accordance with the Third Amendment of 2080 (2023) to the Nepal Citizenship Regulations, 2063 (2006), passed on 4 Ashwin 2080 (21 September 2023).

Office of the Company Registrar published a notice on 10 Bhadra 2080 (27 August 2023) to improvise the work process and devise new work procedure for share allocation, certificate of share register/logbook, transfer of shares through gift deed

The official notice released by the Department of Labour and Occupational Safety to intimate the Department through electronic communication platforms regarding certain instances of non-compliance.
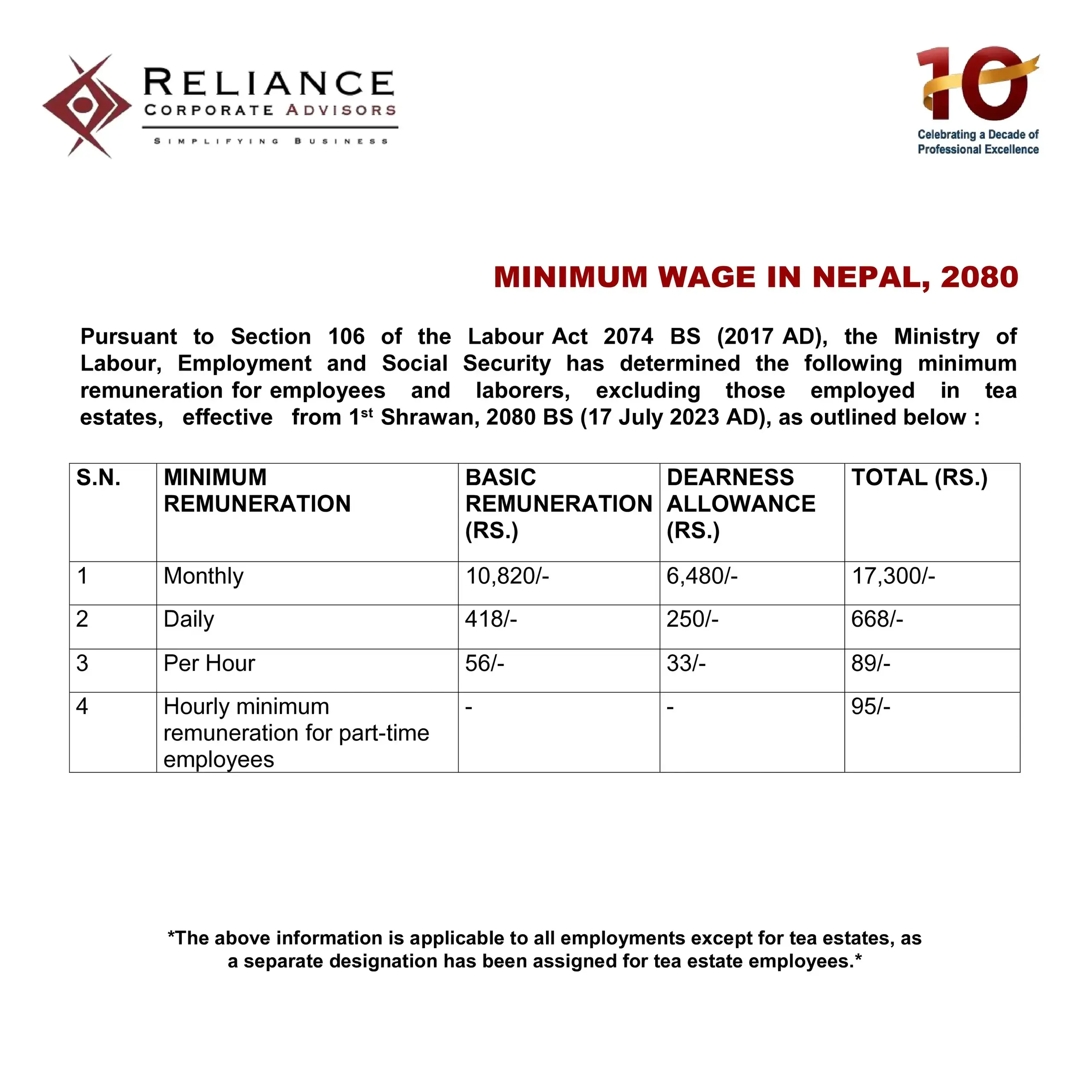
The Ministry of Labour, Employment and Social Security has determined the following minimum remuneration for employees and labours, excluding those employed in tea estates, effective from 1st Shrawan, 2080 BS (17 July 2023), as outlined below

For the fiscal year 2080/81 (2023/24), the Board of Directors of the Social Security Fund unveils the following new interest rates, a key component in the financial landscape, aimed at safeguarding the welfare of members of the society.

Commencing a decade of unwavering professional excellence, Reliance Corporate Advisors (RCA) is committed to streamlining your business operations and addressing all your corporate and legal requirements with the utmost dedication and expertise.
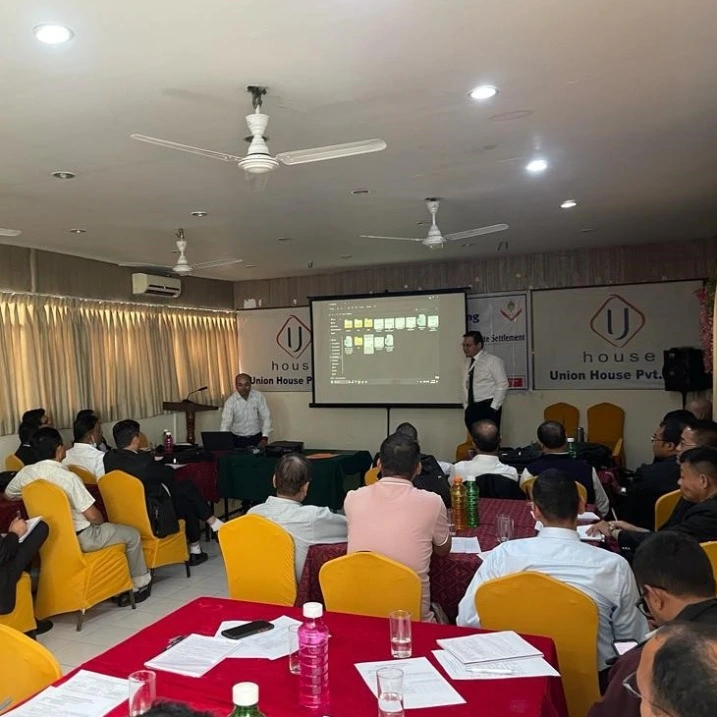

Adv. Prakrit Shrestha conducted a training on contract administration, management and drafting in relation to dispute settlement and arbitration at Union House, Anamanagar on 6 October 2023, organized by the Patan High Court Bar Association. The event saw an interactive participation of prominent lawyers and legal practitioners.

A comprehensive discussion event was organized at the RCA Conference Hall to address the topic of "Social Security Fund (SSF) - Understanding the Benefits and Claim Procedure." This event was spearheaded by the team members of RCA, CA Bishal Panthi, Adv. Dechen Gurung, and Adv. Nikhil Dongol.
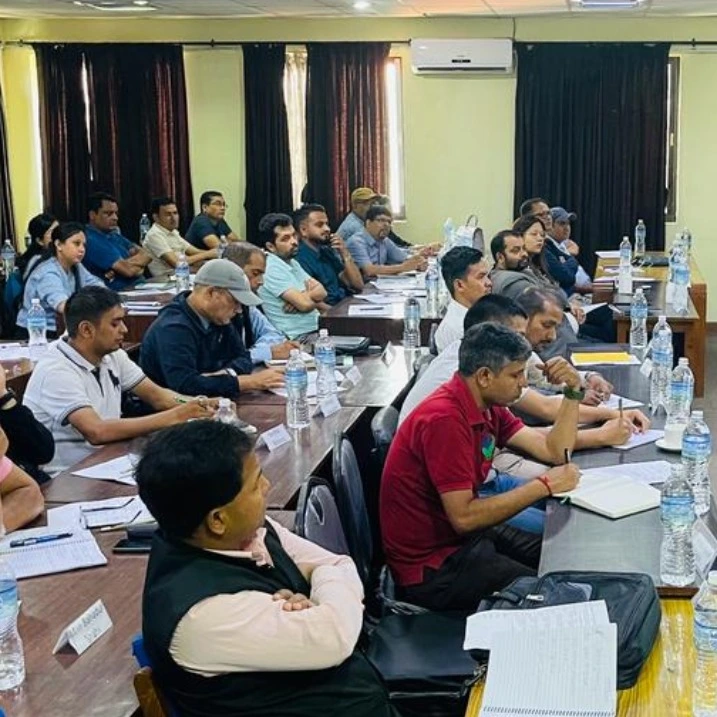

On 10 August 2023, Adv. Prakrit Shrestha conducted a training session on Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) and Arbitration at the Nepal Council of Arbitration (NEPCA). The session highlighted the advantages of arbitration as a dispute resolution method, covered arbitration procedures, and included interactive discussions and case studies.
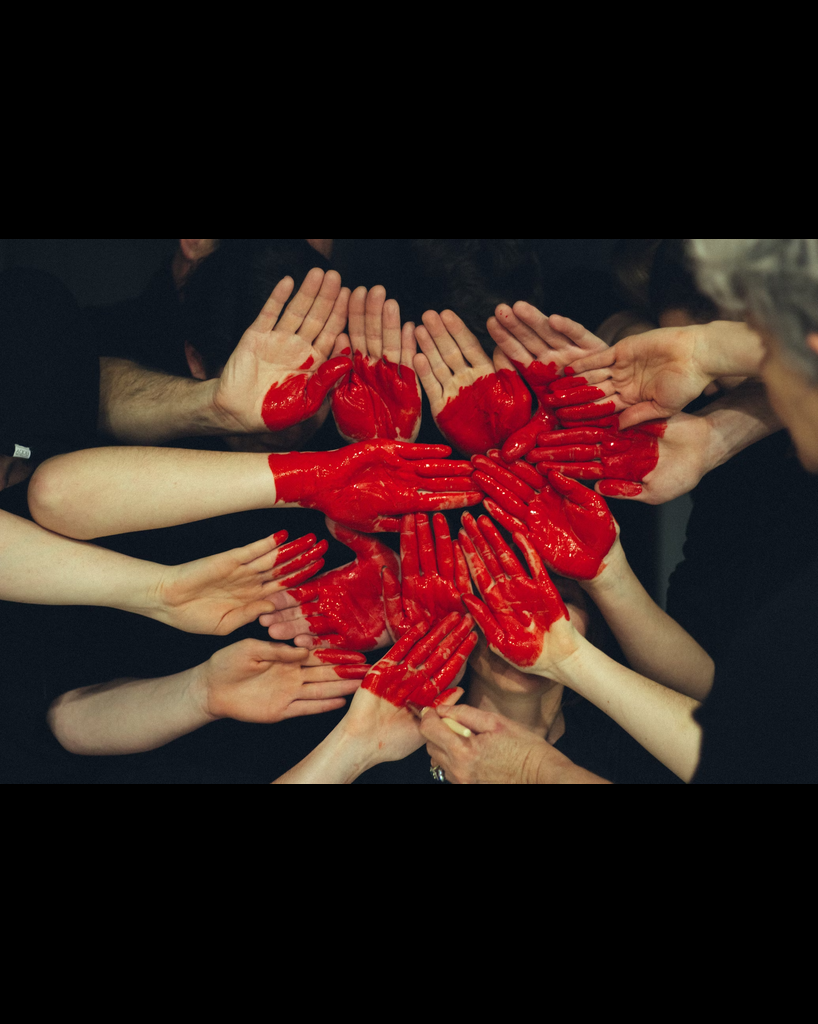

RCA organized a CSR event at Hope Rising Children Home, Mahalaxmi, Lalitpur on 5 August 2023. The day included a wholesome breakfast, engaging games, gift distribution, and a satisfying lunch with the children. RCA's commitment to CSR is driven by the sincere intention to foster a positive and meaningful impact on society.
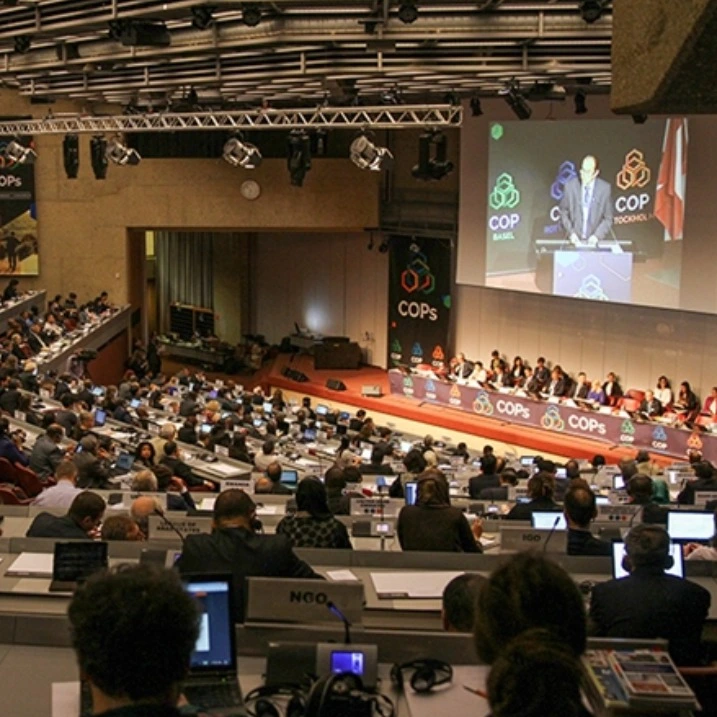

Adv. Prakrit Shrestha, participated in the 16th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Basel Convention, the 11th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Rotterdam Convention, and the 11th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention held from 1-12 May 2023, in Geneva, Switzerland.
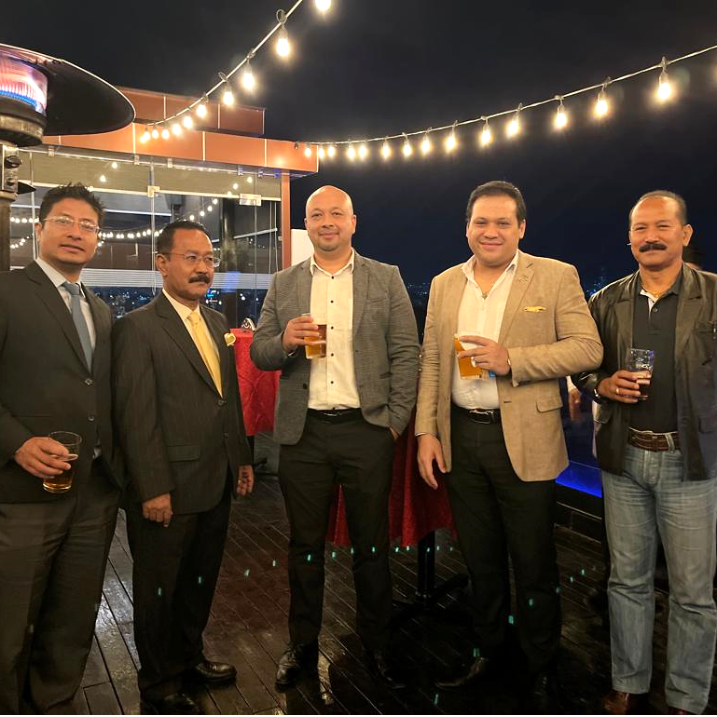

A splendid celebration of Dashain and Tihar was organized by Reliance at Vivanta (by Taj), Jhamsikhel, Lalitpur that brought together a distinguished gathering of Senior Advocates, Advocates, Senior Chartered Accountants, Industrialists and Legal Professionals. A delightful evening of camaraderie in spirit of these important Nepalese festivals.

The Panel Discussion on Intellectual Property Rights and Brands in Nepal, organized by Nepal Youth Chamber and Khabarhub, featured an esteemed panel of experts where the discussion delved into the vital role of intellectual property in brand development in Nepal.